The Historical Origins of ICT vs SMC Trading Strategies
The history of ICT vs SMC begins with the “Inner Circle Trader” mentorships, which introduced the concept that markets are not random but controlled by an algorithm known as the IPDA (Interbank Price Delivery Algorithm). While ICT provided the foundational “source code,” the trading community sought to simplify these dense tutorials.
This simplification led to the birth of the ICT vs SMC debate as Smart Money Concepts (SMC) emerged as a streamlined version of the original teachings. SMC focuses on the “what” and “where,” while ICT focuses heavily on the “when” through time-based elements.
| Era | Methodology | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s-2000s | ICT Origins | IPDA, Time and Price, Market Maker Cycles |
| 2010s | ICT Mentorships | Liquidity Voids, Fair Value Gaps, Killzones |
| 2018-Present | SMC Movement | Order Blocks, Breakers, Simplified Structure |
| Current | ICT vs SMC | Hybrid systems combining time and structure |
Defining the ICT Trading Strategy: The Inner Circle Trader Methodology
The ICT trading strategy is built on the premise that price moves to seek liquidity or rebalance inefficiencies. It is a highly technical framework that requires a deep understanding of the “Market Maker Model.” When discussing ICT vs SMC , the original ICT methodology is often considered more comprehensive but also more difficult to master.
The Power of the ICT Mentorship and Core Logic
The core logic of the ICT mentorship revolves around the idea that “Smart Money” accumulates positions at specific times of the day. In the ICT vs SMC landscape, ICT practitioners prioritize the Killzones , which are specific hours in the New York and London sessions where volatility peaks.
Understanding ICT Liquidity Voids and Fair Value Gaps (FVG)
A Fair Value Gap (FVG) is a three-candle sequence where a price imbalance is created. In the ICT vs SMC context, ICT traders view these gaps as magnets for price. When price leaves a range too quickly, it creates a “void” that must eventually be filled to ensure market efficiency.
Mastering ICT Market Structure Shifts (MSS) and Break of Structure (BOS)
The ICT Market Structure Shift (MSS) is the first sign of a trend reversal. While ICT vs SMC both use structure, the ICT approach looks for the MSS specifically after a liquidity purge. This nuance allows traders to identify high-probability turning points before the broader market reacts.
Defining the SMC Trading Strategy: Smart Money Concepts Explained
The SMC trading strategy is often described as the “retail-friendly” version of ICT. It strips away the complex terminology of the IPDA and focuses on the visual representation of institutional footprints on the chart. In the ICT vs SMC comparison, SMC is praised for its clarity and objective rules.
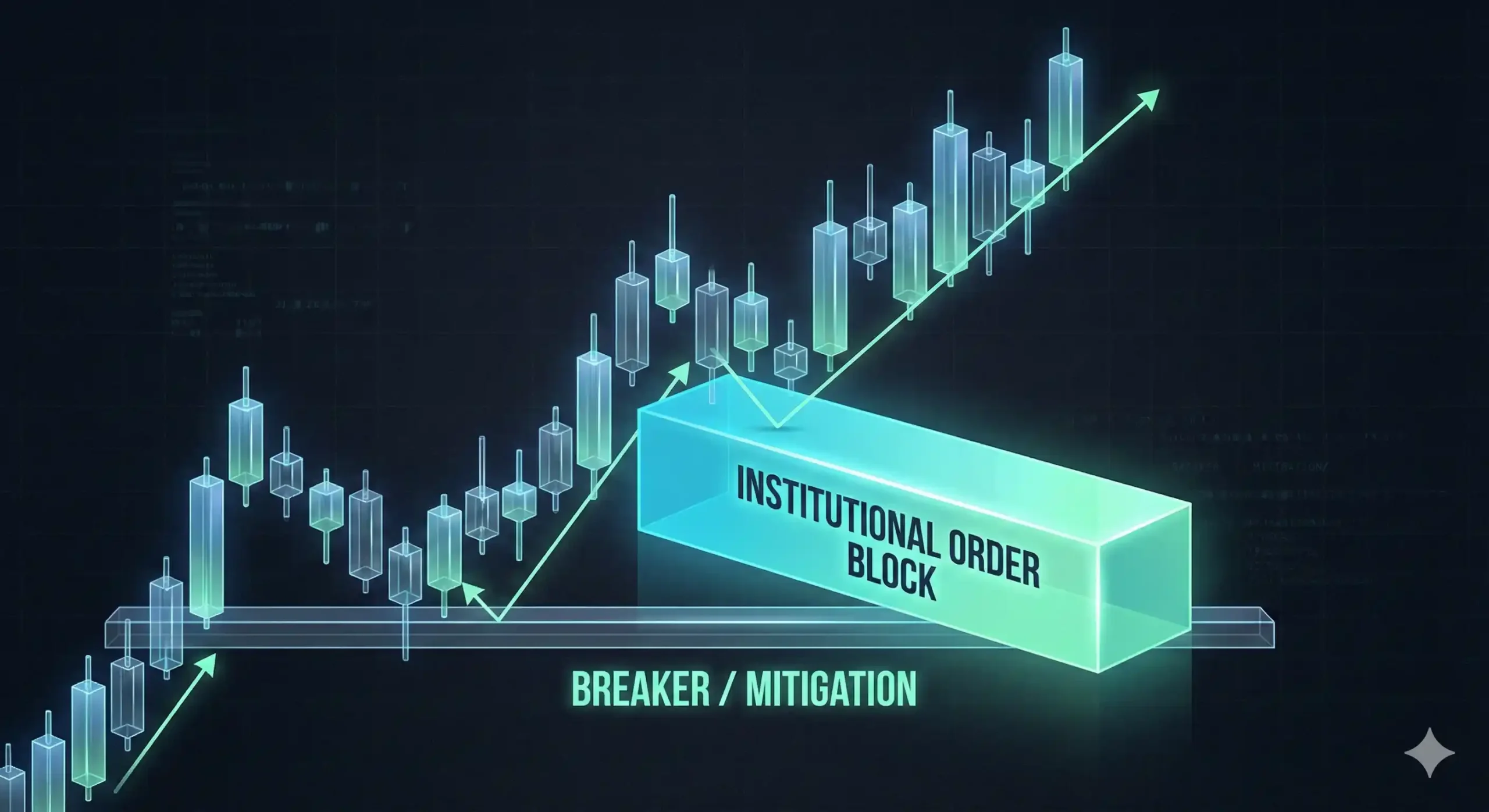
The Evolution of Institutional Order Blocks in SMC Trading Strategy
Order blocks are the final candles before a strong impulsive move. In the ICT vs SMC framework, SMC traders use these blocks as primary entry zones. An institutional order block represents where a large bank has “placed its orders,” creating a zone of high demand or supply.How SMC Trading Strategy Utilizes Supply and Demand Zones
While traditional supply and demand rely on “touches,” the SMC trading strategy looks for “refined” zones. Within the ICT vs SMC debate, SMC traders often focus on the extreme points of a move, looking for the specific candle that initiated a break in market structure.
Mitigating Risk Using SMC Mitigation Blocks and Breakers
Mitigation occurs when a trader exits a losing position at breakeven. In the ICT vs SMC ecosystem, a Mitigation Block is a failed order block. Understanding how these zones flip from support to resistance is a hallmark of a professional SMC trading strategy.

ICT vs SMC: A Deep Dive into Technical Differences
The technical differences in ICT vs SMC often come down to the “Why” versus the “How.” ICT focuses on the “Why” (the algorithm’s intent), whereas SMC focuses on the “How” (the visual structure). Both aim to follow institutional footprints, but their entry triggers differ significantly.
The ICT vs SMC Approach to Identifying Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools are areas where stop losses are clustered, such as previous session highs and lows. In ICT vs SMC analysis, ICT traders look for Buy Side Liquidity (BSL) and Sell Side Liquidity (SSL) . SMC traders typically refer to these as “Equal Highs” and “Equal Lows,” targeting them as exit points.
Which app is better for trading in the UAE? Full Guide for Traders
Comparison of Entry Models: ICT Silver Bullet vs. SMC Choch (Change of Character)
The Silver Bullet is a time-based ICT entry model occurring within specific sixty-minute windows. Conversely, the SMC Choch is a structural shift on lower timeframes. When comparing ICT vs SMC , the Silver Bullet relies on time-confluence, while the Choch relies purely on price action patterns.
Time-Based Confluence in ICT vs SMC (Killzones and London Open)
Time is the “X-axis” of trading that many SMC traders ignore. However, in the ICT vs SMC comparison, ICT emphasizes that price action is meaningless without the correct time. The London Open and New York Open are the only times an ICT trader looks for valid setups.
Advanced ICT vs SMC Market Structure Mapping
For the advanced trader, market structure is more than just “higher highs.” Michael Thorne notes that the distinction between internal and external range liquidity is where most traders fail. In the ICT vs SMC framework, “External” liquidity sits at the major swing points, while “Internal” liquidity exists as FVGs within the swing.
Advanced ICT vs SMC Internal Range Liquidity Management
Managing internal range liquidity requires identifying where price will go after a stop run. In ICT vs SMC strategies, if the external liquidity is purged, price is expected to return to an internal Fair Value Gap. Advanced participants use this “Internal-to-External” flow to predict daily targets.
Complex Fractal Market Analysis in ICT vs SMC Frameworks
Markets are fractal, meaning the same patterns appear on the 1-minute and Monthly charts. The ICT vs SMC approach utilizes this by looking for a HTF (Higher Time Frame) PD Array (Premium/Discount) and then zooming in for a “LTF” (Lower Time Frame) entry.
Risk Management and Psychology in ICT vs SMC
No strategy survives without risk management. In the ICT vs SMC world, the high reward-to-risk ratios can lead to a low win rate, which challenges a trader’s psychology. Professional traders prioritize capital preservation over “catching the exact wick.”
Stop Loss Placement in ICT vs SMC Entry Models
Stop losses in ICT vs SMC are typically placed above or below the candle that created the displacement. In ICT, the stop might be placed at the “Mean Threshold” (50%) of an order block. In SMC, it is often placed strictly at the swing high or low.
Determining R:R (Risk-to-Reward) Expectations in ICT vs SMC Strategies
Both ICT vs SMC methodologies often boast R:R ratios of 1:5 or higher.
ICT vs SMC Comparison Table for Institutional Traders
To choose between ICT vs SMC , one must understand the operational requirements of each.
| Feature | ICT (Inner Circle Trader) | SMC (Smart Money Concepts) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Toolset | Fair Value Gaps, Power of 3, Killzones | Order Blocks, Choch, BOS |
| Terminology | High Complexity (PD Arrays) | Moderate Complexity (Supply/Demand) |
| Timeframe | Multi-timeframe with “Time” focus | Multi-timeframe with “Structure” focus |
| Difficulty | High (Steep learning curve) | Moderate (Visual/Pattern based) |
| Best For | Intraday Scalpers | Swing and Day Traders |
Backtesting Results: ICT vs SMC Profitability Analysis
Backtesting the ICT vs SMC models reveals distinct performance characteristics. Data suggests that ICT models perform exceptionally well in high-volatility sessions, while SMC models are more robust during trending markets across various asset classes.
Data-Driven Performance of the ICT Trading Strategy in Forex
The ICT trading strategy excels in the Forex market due to the high volume during London and New York sessions. In ICT vs SMC testing, ICT entries during “London Close” often provide high-probability reversals that SMC structure alone might miss.
Backtesting the SMC Trading Strategy Across Indices and Crypto
The SMC trading strategy shows strong results in S&P 500 and Nasdaq futures. Because these markets trend aggressively, the SMC “Break of Structure” and “Trend Continuation” models within the ICT vs SMC framework provide clear, repeatable signals.
Which is Better for Your Career: ICT vs SMC?
Choosing between ICT vs SMC depends on your personality. Do you prefer a rules-based, time-sensitive system (ICT), or a more flexible, structure-oriented approach (SMC)? Both can lead to a successful career in proprietary firm trading.
Pros and Cons of the Original ICT Trading Strategy
- Pros: Precision entries, deep understanding of market logic, high R:R.
- Cons: Steep learning curve, thousands of hours of video content, can lead to “analysis paralysis” within the ICT vs SMC context.
Pros and Cons of the Streamlined SMC Trading Strategy
- Pros: Cleaner charts, faster to learn, easier to automate.
- Cons: Can be “retailized,” may ignore the crucial “Time” element of ICT vs SMC logic, leading to false breakouts.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About ICT vs SMC
Is ICT vs SMC the same thing for beginner traders?
While they share the same DNA, they are not the same. In the ICT vs SMC debate, think of ICT as the “Source Code” and SMC as the “User Interface.” Beginners often find SMC easier to grasp initially.
Which is more profitable, the ICT or SMC trading strategy?
Profitability depends on the trader, not the label. However, ICT vs SMC data suggests ICT may offer higher precision for scalping, while SMC offers more consistency for those who cannot watch the charts during specific hours.
Can you combine ICT vs SMC into a single trading system?
Yes. Most professional traders use a hybrid ICT vs SMC approach, using ICT’s “Killzones” for timing and SMC’s “Order Blocks” for entry zones.
Do institutional banks actually use ICT vs SMC concepts?
Banks use algorithmic execution. While they don’t call it “ ICT vs SMC ,” the concepts of “Liquidity Sweeps” and “Rebalancing” are exactly how institutional algorithms are programmed to minimize slippage.
Conclusion: Final Verdict on ICT vs SMC for Advanced Market Participants
The choice between ICT vs SMC ultimately comes down to your commitment to the craft. ICT offers a masterclass in market theory, while SMC provides a functional toolkit for the modern trader.
Whether you choose the complex depth of the ICT trading strategy or the refined execution of SMC, the key is consistency in identifying institutional intent.

A stock market enthusiast with hands-on experience in trading. He writes simple and practical content to help people understand the market better.


